半透明混合
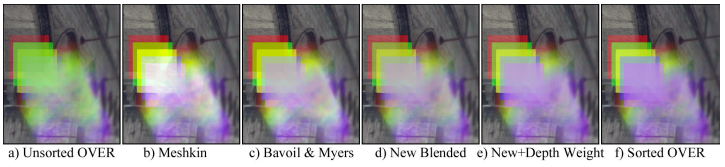
1. OVER
1.1. Porter & Duff OVER
一个表面覆盖背景
其中,
背景的贡献为
备注: 公式
2. Blended OIT
2.1. Meshkin’s Method
Meshkin首次引入blended OIT, 支持交换操作,
// OpenGL伪代码 - 浮点RenderTarget
drawOpaqueSurfaces();
copyColorBufferToTexture(C0Texture);
glDepthMask(GL_FALSE);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_ONE, GL_ONE);
bindFragmentShader("
...
uniform sampler2D C0Texture;
void main() {
...
vec3 C0 = texelFetch(C0Texture, ivec2(gl_FragCoord.xy), 0).rgb;
gl_FragColor = vec4(Ci - ai * C0, 1.0);
}", C0Texture);
drawTransparentSurfaces();当α很小且所有颜色很接近时, 结果接近back-to-front排序OVER操作.
当α较大时, 背景强度和净覆盖率可能与OVER操作有较大偏差.
2.2. Bavoil and Myers’ Method
Bavoil and Myers用一个更好的颜色及覆盖率近似, 改进了Meshkin的操作, 权重平均如下
// OpenGL伪代码
drawOpaqueSurfaces();
bindFramebuffer(accumTexture, countTexture);
glDepthMask(GL_FALSE);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_ONE, GL_ONE);
bindFragmentShader("...
gl_FragData[0] = vec4(Ci, ai);
gl_FragData[1] = vec4(1);
...}");
drawTransparentSurfaces();
unbindFramebuffer();
glBlendFunc(GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA, GL_SRC_ALPHA);
bindFragmentShader("...
vec4 accum = texelFetch(accumTexture, ivec2(gl_FragCoord.xy), 0);
float n = max(1.0, texelFetch(countTexture, ivec2(gl_FragCoord.xy), 0).r);
gl_FragColor = vec4(accum.rgb / max(accum.a, 0.0001),
pow(max(0.0, 1.0 - accum.a / n), n));
...}", accumTexture, countTexture);平均了所有组合的表面, 改善了
但引入一个问题, 当引入
2.3. A New Blended OIT Method
改善了
组合的部分覆盖表面的颜色始终由覆盖率最高的表面主导,无论它们出现在深度排序中的哪个位置
2.4. Depth Weights Improve Occlusion (Weighted Blended)
引入了深度权重, 颜色权重离相机越远越小
其中,
所以
文章推荐了几个通用的权重函数,在任意场景大深度下表现都不错,
其中,
每个公式都进行了值域裁剪,原因是在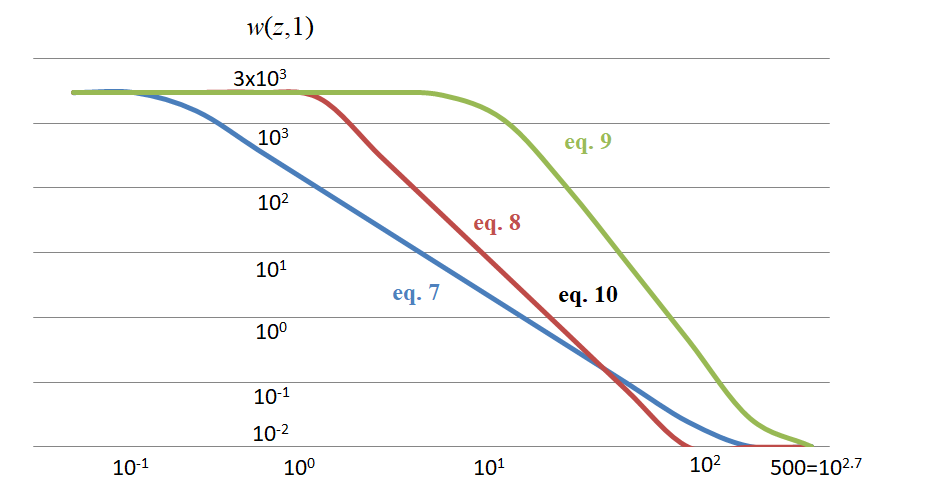
// OpenGL伪代码
drawOpaqueSurfaces();
clear accumTexture to vec4(0), revealageTexture to float(1)
bindFramebuffer(accumTexture, revealageTexture);
glDepthMask(GL_FALSE);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunci(0, GL_ONE, GL_ONE);
glBlendFunci(1, GL_ZERO, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
bindFragmentShader("...
gl_FragData[0] = vec4(Ci, ai) * w(zi, ai);
gl_FragData[1] = vec4(ai);
...}");
drawTransparentSurfaces();
unbindFramebuffer();
glBlendFunc(GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA, GL_SRC_ALPHA);
bindFragmentShader("...
vec4 accum = texelFetch(accumTexture, ivec2(gl_FragCoord.xy), 0);
float r = texelFetch(revealageTexture, ivec2(gl_FragCoord.xy), 0).r;
gl_FragColor = vec4(accum.rgb / clamp(accum.a, 1e-4, 5e4), r);
...}", accumTexture, revealageTexture);// OpenGL伪代码 - Without Per-Render Target Blending
drawOpaqueSurfaces();
bindFramebuffer(A, B);
glColorClearValue(0,0,0,1);
glClear();
glDepthMask(GL_FALSE);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFuncSeparate(GL_ONE, GL_ONE, GL_ZERO, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
bindFragmentShader("...
gl_FragData[0] = vec4(Ci * w(zi, ai), ai);
gl_FragData[1].r = ai * w(zi, ai);
...}");
drawTransparentSurfaces();
unbindFramebuffer();
glBlendFunc(GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA, GL_SRC_ALPHA);
bindFragmentShader("...
vec4 accum = texelFetch(ATexture, ivec2(gl_FragCoord.xy), 0);
float r = accum.a;
accum.a = texelFetch(BTexture, ivec2(gl_FragCoord.xy), 0).r;
gl_FragColor = vec4(accum.rgb / clamp(accum.a, 1e-4, 5e4), r);
...}", A, B);一些限制
在下列情况下Blended OIT方法表现质量会受到影响
1.场景中深度范围很大,在单个pass中提交多个半透明紧密结合的群体;在这种情况下, 很难选择既能够区分单个集合,还能够在集合中区分半透明层的深度函数
2.方法和深度相关,也就是半透明的mesh放在相机近处和远处颜色会有所差异,例如将整个场景移动到不同的深度范围可以改变其颜色,但这种差异一般是可以接受的, 因为随着对象在z轴上移动,颜色过渡会缓慢发生
前提假设
1.部分覆盖的位置在层级间不相关, 类似自遮挡、互相遮挡情况(Porter And Duff上假设)
2.表面要么具有相似的颜色, 要么深度相对分布均匀
3.颜色精度对于靠近的表面最重要,但在整个深度范围内精度都很重要
3. 参考
1.半透明顺序无关渲染 OIT
2.Weighted Blended Order-Independent Transparency
3.顺序无关的半透明混合(OIT)相关方法
4.实现一个较新的OIT方法 Per-Pixel Linked Lists
5.Antialiased Deferred Rendering